ARTICLE AT A GLANCE
Tracking Heart Rate Variability (HRV) over time can be a useful tool in identifying imbalances in our autonomic nervous system (ANS), which regulates many aspects of our biology including all aspects of our cardiovascular system like blood pressure, heart rate, etc.
HRV FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
What is heart rate variability (HRV) ?
What do HRV scores mean?
Why should I track HRV?
Is HRV linked to health and well-being?
Why do athletes and coaches care about HRV?
How is HRV calculated?
What is a good HRV score in MS?
Is low HRV dangerous?
How do I improve my HRV score?
Who makes the most accurate HRV monitor?
What is heart rate variability (HRV)?
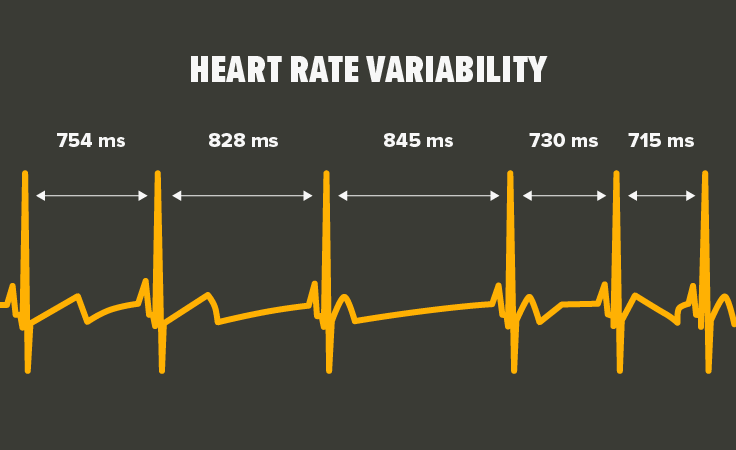
Heart rate variability is the measure of the variation in time between heartbeats. Unlike basic heart rate (HR) that counts the number of beats per minute, HRV looks much closer at the exact changes in time between successive beats and the balance between sympathetic and parasympathetic tone.
The sympathetic nervous system prepares the body for intense physical activity (fight-or-flight) and the parasympathetic nervous system relaxes the mind and body.
The variation in your heartbeats within milliseconds (ms) reflects this balance.
What do HRV scores mean?
Low HRV: If the intervals between your heartbeats are relatively constant, then you are in a fight or flight state and your HRV is low.
High HRV: If the interval length variates, you are in a more relaxed state and your HRV is high. This is associated with good recovery.
Why should I track HRV?
Tracking HRV over time can be a useful tool in identifying imbalances in our autonomic nervous system (ANS), which regulates many aspects of our biology including all aspects of our cardiovascular system like blood pressure, heart rate, etc.
Our body handles the stress of everyday life through two subcategories of our ANS, our sympathetic (SNS; fight-or-flight) and our parasympathetic (PNS; relaxation) systems.
Our ANS responds to negative stimuli such as stress, poor sleep, and unhealthy diets, but also to positive stimuli such as good news, seeing a loved one, or having a nourishing meal.
If your SNS tends to be activated more often, that can be seen in a low HRV, meaning less variance in the time between heart beats. The more often our PNS is activated, the more relaxed we are, and we see an increase in HRV.
Those with a higher HRV may have a high level of fitness and be more resilient to stress. Our SNS response to stress focuses on the short-term survival. This acute response can become chronic in modern daily life with stresses related to in work, relationships, financial, lifestyle, etc.
Chronically accumulated stress from multiple sources can all contribute to drastically reduced health and performance long term.
Is HRV linked to health and well-being?
People who have a higher HRV score may have greater cardiovascular health, less inflammation and be more resilient to stress. HRV might also be used to suggest an early diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes and be a meaningful marker to show the effectiveness of treatment for various metabolic disorders including a better diet and more activity.
HRV can drop substantially when you get sick and can stay low even after you feel better indicating that your body is still recovering.
Pretreatment HRV has helped predict outcomes of treatment strategies for people with anxiety and depression by determining which patients could benefit from antidepressants and which patients may require a different treatment approach.
Since HRV can help create more awareness of how healthy habits make a positive impact on your score, it’s likely that this will influence behavioral change for many.
Why do athletes and coaches care about HRV?

Athletes are often exposed to new training programs, rigorous travel schedules and blocks of competition that may be significantly tougher than in previous weeks. Any of these factors alone can test their ability to recover.
Differences in hormone levels, diets, outside stressors and sleep quality further complicate a “one size fits all” plan for optimal performance.
To manage stress, we need to measure stress. HRV data can be used to determine when an athlete is less likely to perform at their best or even suggest a higher risk for injury.
As a coach, HRV data may help your staff make decisions on who to place in the starting lineup on a given day. This information is validating just how important personalization is for long term athletic success
How is HRV calculated?
The standard method to measure HRV is through an electrocardiogram.
ECG (Electrocardiogram) – The ‘R’ peak in the QRS complex measured by ECG marks a heartbeat. The time between two R’s is known as the RR Interval. This is measured when a stress test or a VO2Max test is performed with a 12-lead monitor.
We no longer need an ECG to measure HRV as many companies now provide the means through photoplethysmography (PPG) in wearable technology.
Most smart watches use an optical technique that detects blood volume changes under the skin surface to calculate an HRV score.
PPG (Photoplethysmography) – Measures inter-beat intervals or IBIs. This marks the time from the steepest increase in signal prior to the completion of the ventricular contraction (heartbeat). PPG determines the timing of cardiac cycles via continuous monitoring of changes in blood volume in a portion of the peripheral microvasculature.
What is a good HRV score in MS?
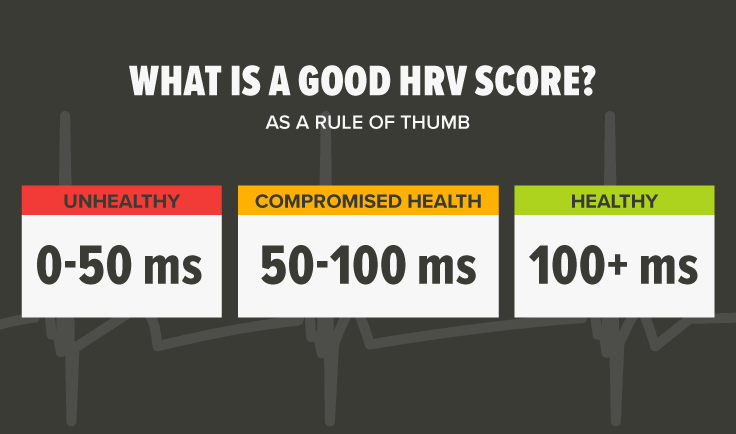
A good HRV score is relative for each person. HRV is a highly sensitive metric and responds uniquely for everyone. As a rule of thumb, values below 50 ms are classified as unhealthy, 50–100 ms signal compromised health, and above 100 ms are healthy. A higher HRV correlates with better health, resilience, and increased fitness.
Is low HRV dangerous?
A low HRV reading isn’t always bad. For example, a tough workout or an occasional bad night of sleep can cause a low score. For most healthy individuals, your score will return back to normal or better within a few days.
Chronically low heart rate variability is generally not favorable though and can indicate declining health, illness, chronic stress or overtraining.
Having a low HRV has been shown to be a risk factor for many issues including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, depression, and even death.
While low HRV can be a signal of illness, monitoring your HRV patterns gives you a more complete picture of your overall health.
How do I improve my HRV score?
You can improve your HRV score by focusing on habits that improve your overall health like proper nutrition, exercise, maintaining healthy stress levels and getting 8 hours of sleep nightly.
Who makes the most accurate HRV monitor?
The three most popular HRV monitors are:
1. Oura Ring
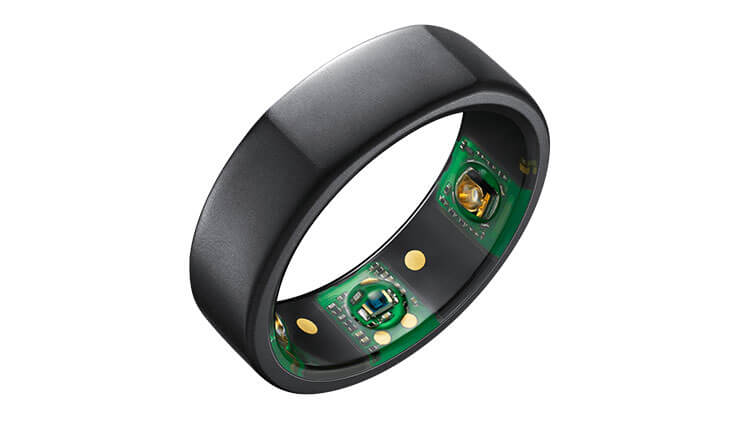

- 24/7 wearable ring
- Recommended for any health-conscious person.
- Gives more data than just HRV and HR, such as body temperature and sleep quality, etc.
2. Whoop Strap
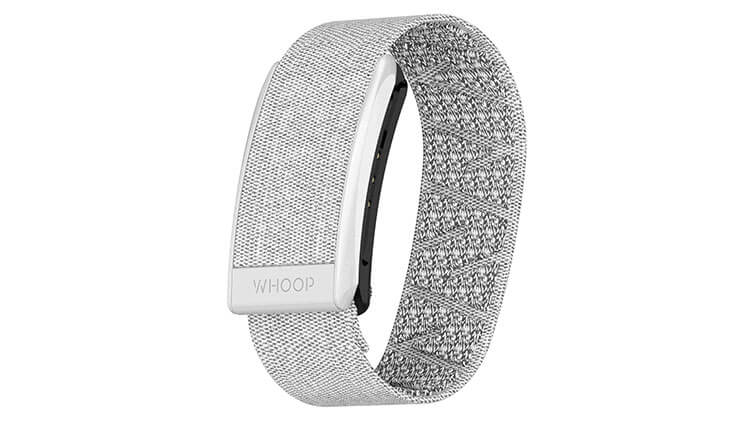

- 24/7 wearable
- Recommended for athletes
- Waterproof
- Requires monthly membership.
- Measures and coaches you through strain, recovery, and sleep
3. CorSense by Elite HRV
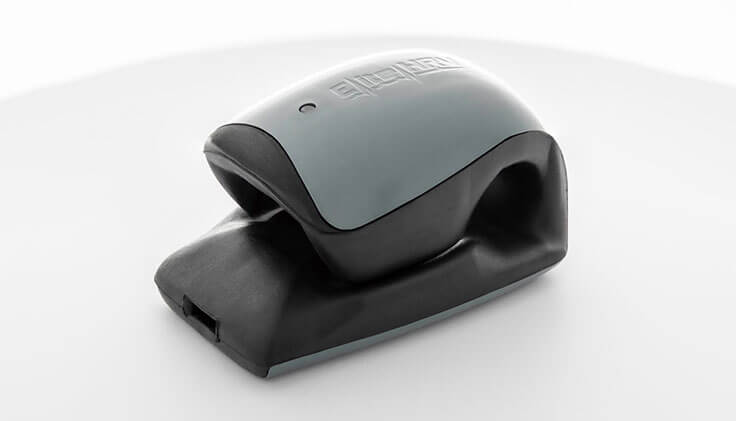

- Finger sensor
- 2-minute reading first thing in the morning
- Only tracks HR and HRV






